Below are my write-ups for the Pokeball Escape and Bleep challenges that were part of UMDCTF 2023.
Pokeball Escape
After decompiling the Pokeball Escape application using JADX, we get the following code in the com.example.pokeballescape.MainActivity class:
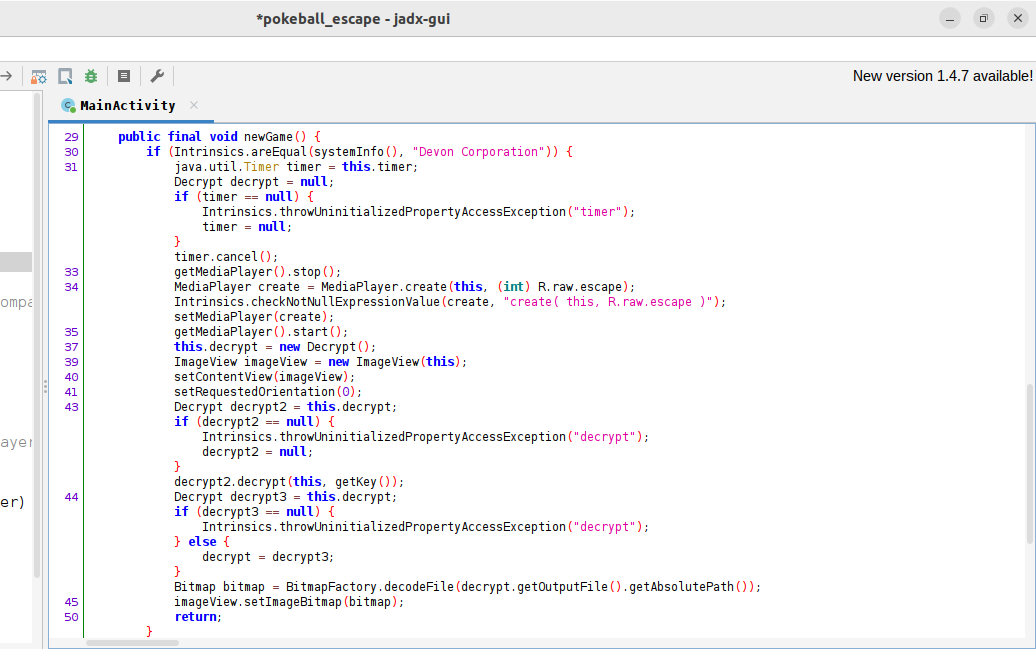
If the value returned by the systemInfo() function is equal to Devon Corporation, the method proceeds to cancel any running timer, stop any playing media player, and create a new media player using a sound file called escape. It then sets this media player as the current media player and starts it. Next, it creates a new instance of the Decrypt class and an instance of the ImageView class, receives a file from decrypt.getOutputFile(), and sets it into the ImageView.
Let’s take a look at the code present in the Decrypt class:
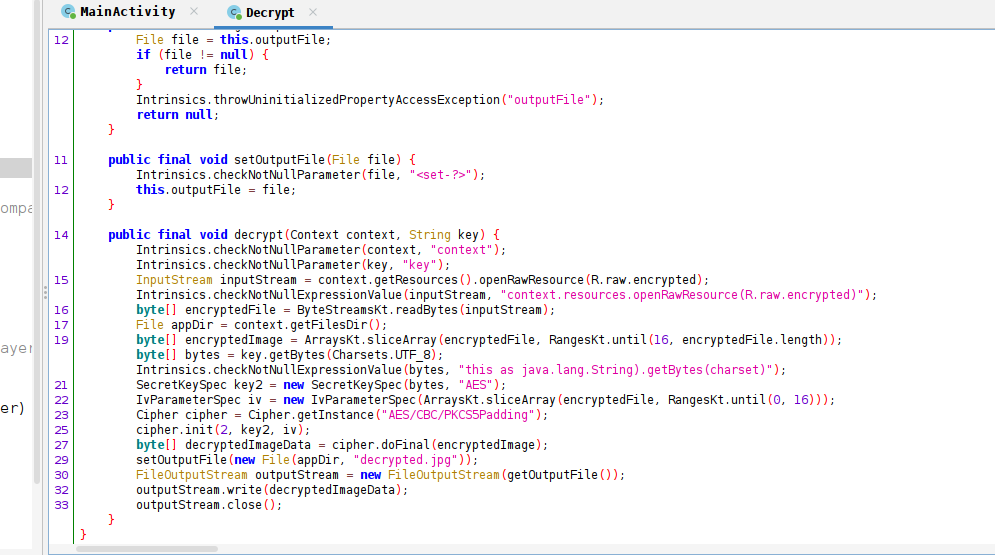
The program reads a binary file called “encrypted,” extracts the first 16 bytes from it, and uses them as an initialization vector (IV) for the AES decryption process. The AES key used in the decryption process is returned by the getKey() function, which is a native function. Lastly, the program decrypts the remaining bytes of the file using AES-CBC.
1 | private final native String getKey(); |
The code of native functions are stored in shared libraries. Let’s use apktool to extract the contents of the apk and grab the shared libraries.
1 | apktool d pokeball_escape.apk |
The shared libraries are present in pokeball_escape/lib directory. Let’s create a new project in Android Studio and log the value of the key. The package name of the project must be com.example.pokeballescape.

Adding the libraries into the appropriate folder as shown above, according to the architecture, we can log the value returned by the getKey() function.

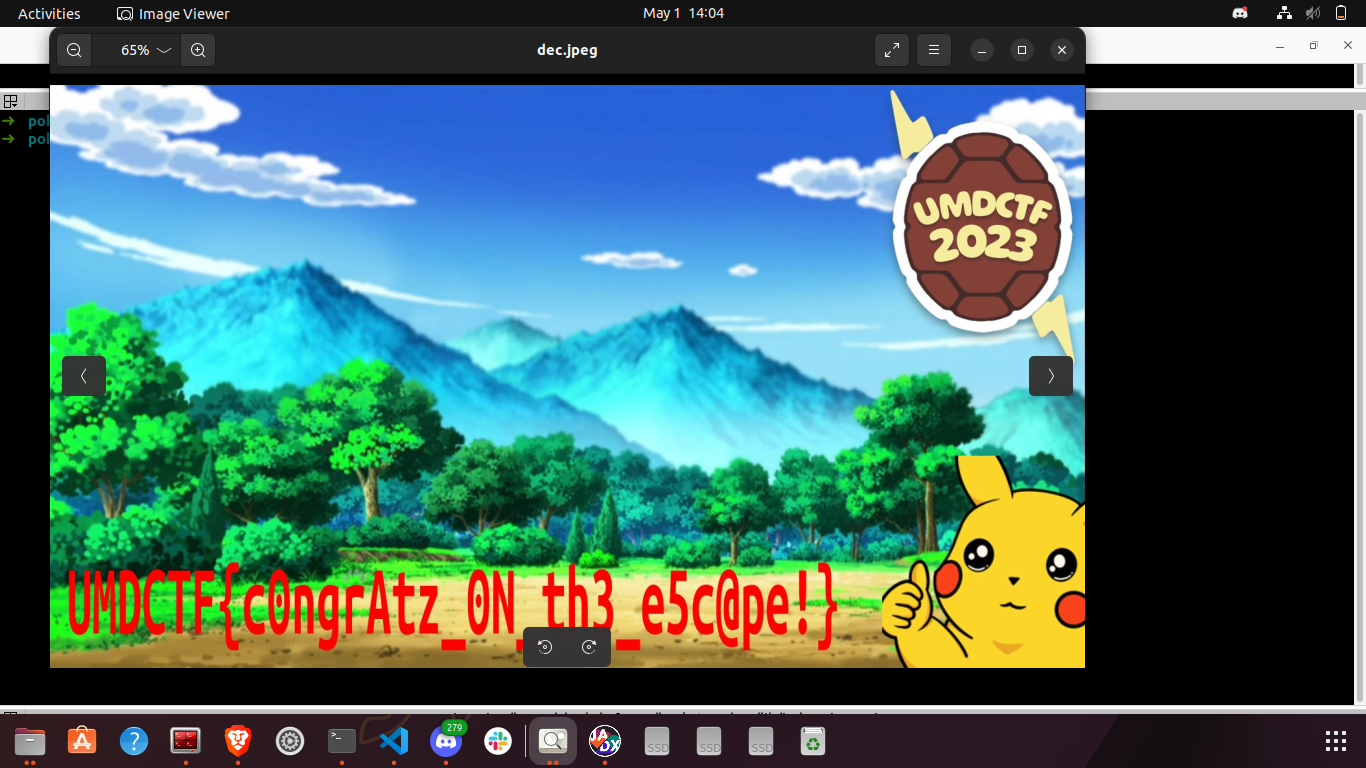
This gives us the key Tih5qqfWmdPbiXoLZAiEa6epQccUXnPQ. We can retrieve the encrypted file from pokeball_escape/res/raw/encrypted and create a simple Python script to decrypt it.
1 | from Crypto.Cipher import AES |
Bleep
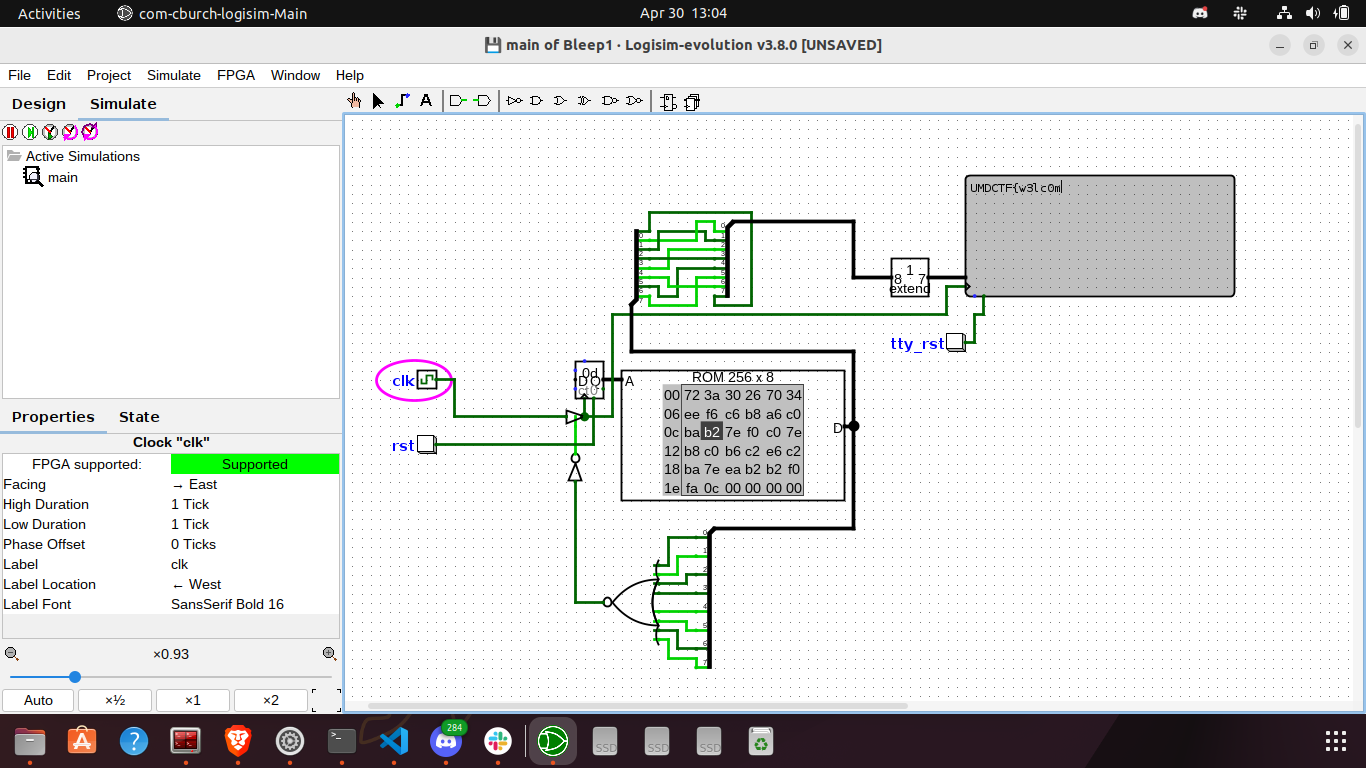
In this challenge we were given a Bleep1.circ file and a flag.enc file. .circ files are circuit files that are used by Logisim, which is an open-source tool used for designing and simulating digital logic circuits. After loading Bleep1.circ in Logisim, we get the following circuit diagram.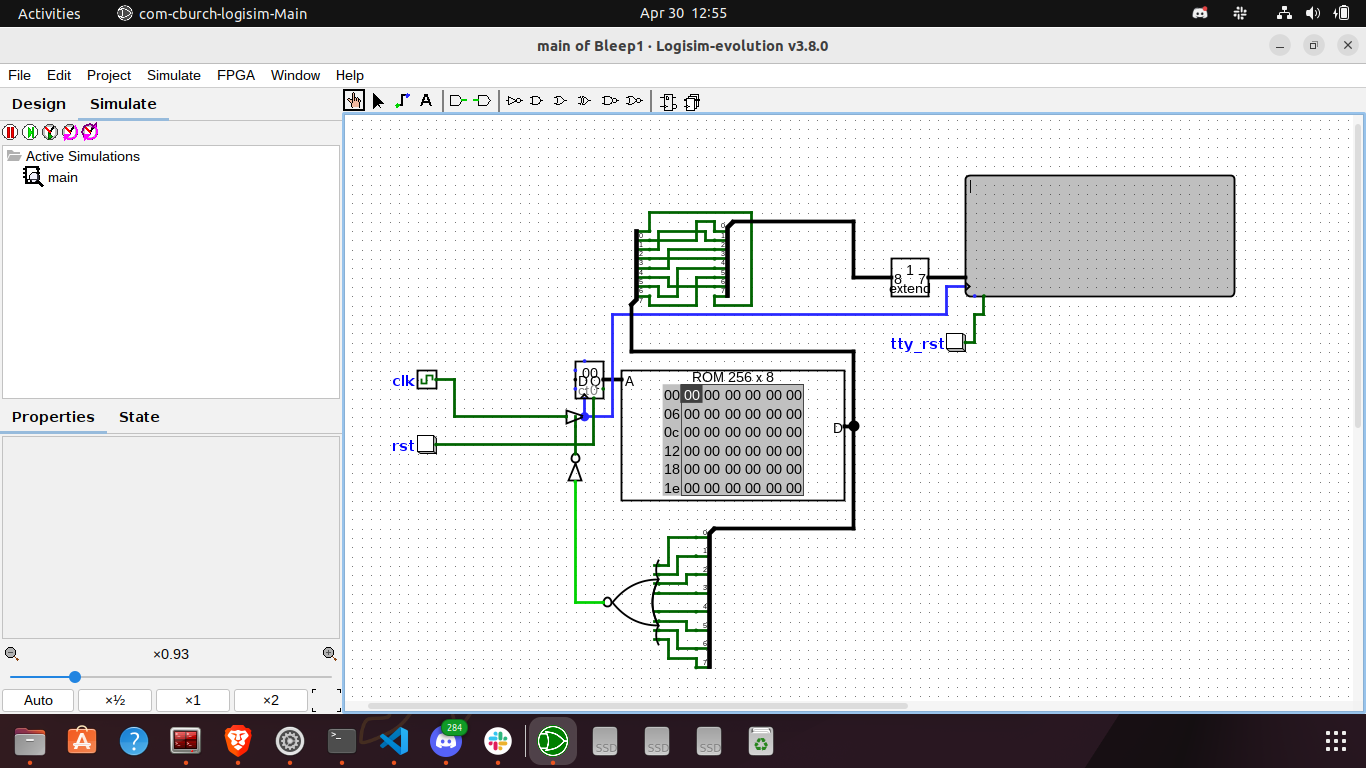
The contents of flag.enc are a bunch of hexadecimal numbers 723a30267034eef6c6b8a6c0bab27ef0c07eb8c0b6c2e6c2ba7eeab2b2f0fac. After inserting these values into the ROM, we can click on the clock (labelled as clk) to get the flag, one character at a time.